When the Canadian prime minister Justin Trudeau visited the White House in 2016, the French part of his speech translated by ABC TV’s speech recognition software was riddled with quirks ranging from suave “portfolio of us old guys” to cryptic “agreeing. 032. clearing.” It wasn’t the finest performance of AI translation, but hey, everybody has to start somewhere.
After years of development, artificial intelligence tools seem to be finally catching up with professional translators and interpreters. With over 1 billion users, Google Translate is now the most popular translation service out there, with an impressive accuracy of up to 90%.
But where did it all start?
Will artificial intelligence replace translators?
If an AI translates a recipe, will it still taste as good? (just kidding)
Here’s everything you wanted to know about AI translation technology but were afraid to ask.
Table of Contents
🤖 💬 How AI Translation Works
Machine translation (MT) — the use of computers to automatically translate text — has been around since at least the 1950s. It all started when researchers at Georgetown university translated 60 Russian words to English using an IBM 701 mainframe computer.(1)
But science fiction writers had figured it out much earlier.
In a 1945 novella First Contact, writer Murray Leinster played with the concept of a “universal translator,” a device that could translate speech between human and alien languages.

The first real-world attempts at machine translation were rather primitive, at least by the standards of space-traveling, technically advanced alien races. But they opened the door to a wave of funding and sparked public interest, at least for a short while.
During the Cold War, a rule-based translation system called SYSTRAN was used to translate simple sentences from Russian to English. SYSTRAN leveraged w hat’s knows as rule-based machine translation (RbMT) that involves sets of linguistic rules and bilingual dictionaries.(2)
In the 1990s, machine translation shifted to statistical models utilizing large amounts of data to learn patterns in languages and to make predictions about how words and phrases are translated. To train those models, researchers fed” them large amounts of data including bilingual corpora, a collection of parallel texts in two different languages.(3)
The researchers involved in the Georgetown-IBM experiment predicted that it would take 3 to 5 years to fully develop MT technology. Well, it took six decades of hilarious mistranslations, awkward phrasing, and occasionally downright offensive results to make a breakthrough.
In 2016, Google announced that they developed a neural machine translation (NMT) system capable of producing much more accurate and fluent translations. The NMT system was based on a type of artificial neural network, which allowed the system to “learn” patterns and structures in language more effectively than rule-based or statistical machines.(4)
Today, NMT is the dominant, and so far the most accurate, translation technology in the space. NMT systems can not only “understand” the complexity of natural languages, but they can also accurately render technical vocabulary, including legal, medical, and scientific terminology.
“Ok, so are AI tools already better than human translators?” Not yet, but they come with some pretty compelling benefits that are simply too good to ignore.
🚀 The Benefits of AI Translation
Improved Communication
When the Persians invaded Greece in 490 BCE under the command of King Darius I, they brought interpreters to communicate with the local population. These days, they would probably simplify the logistics and use smartphones with a stable Wi-Fi connection instead.
Machine translation has become the go-to tool for breaking the language barrier, whether it’s for negotiating peace treaties or ordering a bowl of noodles from a street vendor.
But did you know that AI is also hard at work helping you learn new languages?
For instance, the language-learning app Duolingo employs machine learning and natural language processing in the course creation process. The company uses their “Birdbrain” model to personalize the learning experience, track user progress, and… generate answer variations.(5)
Now you know why “you’re crying and the onion is laughing.” 🧅
Increased Global Reach
We live in a global market where you can order a product from the other side of the world and have it shipped to your doorstep faster than you can say “international shipping fees.”
In large part, we have to thank AI tools for making that possible.
According to a 2023 report by Unbabel titled “Global Trends in Marketing Localization,” 39% of marketers are using machine translation in localization strategies. And that makes a lot of sense since 84% of companies say content localization has a major impact on revenue growth.(6)
The spread of machine-translated content is also a powerful driver of engagement that can make or break a business. Research has shown that 40% of people won’t make a purchase if the information about the product or service is not available in their language.(7)
Flexibility and Cost Savings
These days, machine translation can handle large amounts of data with ease and can seamlessly integrate with existing workflows and systems. This is great news for businesses with global customer bases, as it means they can easily reach customers in different parts of the world.
“Isn’t that expensive?” Well, not anymore.
AI systems have reached a point where they are more affordable than human translators. The average cost of a professional translation service ranges between $0.10 and $0.30 / word. Amazon Translate API charges $15.00 per million characters and some terrifying accuracy.
AI still flunks the “translate this pick-up line to work in every language” test, but it’s getting there.
🧐 The Challenges of AI Translation
The Bible has been subject to many mistranslations throughout history. One of the most bizarre mishaps was a mistranslation of the King James Version of the Bible where the Hebrew word “qeren” (meaning “beam of light”) was mistranslated as “horn” in Exodus 34:29-35.
That led to the many portrayals of Moses with horns, like this one.

Image credit: Jörg Bittner Unna
So, how does AI translation technology stack up against that?
Translation Error Rate (TER) and BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy) are two key metrics for evaluating machine translation. In 2021 researchers at UCLA found that Google Translate is 82.5% accurate in translating medical terms. That would be impressive if not for the fact that the accuracy ranged between 55% and 94% depending on the language.(8)
Of course, the blunders of machine translation can happen in less specialized use cases.
Natural languages are infinitely complex, with nuances in grammar, syntax, and vocabulary that may sometimes be difficult to capture and accurately render with machine translation.
You may not encounter words like Japanese “kintsugi” (“repairing broken pottery with gold or silver lacquer”) or Danish “hygge” (“contentment in one’s surroundings”) too often. But when you do, you want to render them in your own language without losing the cultural context.
But that doesn’t mean you have to resort to spending endless nights hunched over dusty tomes like a medieval monk (unless that’s your thing, of course).
AI translation tools are an excellent addition to any workflow. If used the right way, they can help you streamline the translation process, improve accuracy, and boost productivity. Just so you can indulge in some “dolce far niente” — the sweet art of doing nothing. 🤷♂️
🐑 Using Taskade to Translate Content
Whether you’re working on a DIY project or collaborating with a global team, you may need a little help to overcome linguistic barriers. This is where Taskade AI comes into play.
Taskade AI is our writing assistant powered by GPT-3.5, a powerful language model developed by OpenAI. With the help of Taskade AI, you can now easily translate text into a number of languages without having to copy text between windows or, well, brandish a dictionary.
Here’s how it works.
Open a Taskade project and paste in or type the text you want to translate. Next, type /translate in the same line and choose one of the available languages. Taskade AI can currently translate your projects into 12 languages, including English, Japanese, and Spanish.
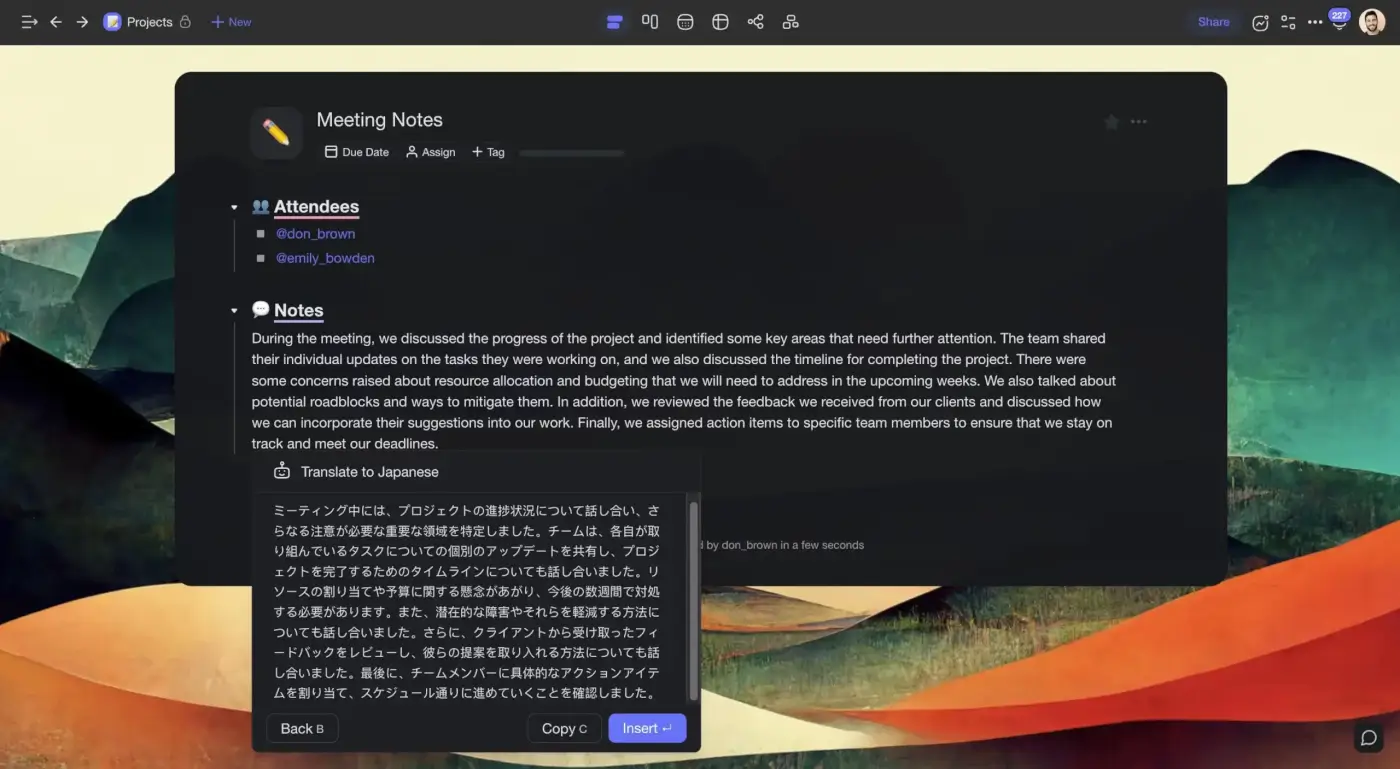
Et voilà ! (in case you’re wondering, that means “there you go!” in French).
Taskade AI is an excellent companion tool for translating:
- 💰 Marketing materials (brochures, flyers, social media posts, email newsletters)
- 📑 Reports and documents (business plans, project proposals, whitepapers)
- 🛒 E-commerce product listings (product descriptions, features, specifications)
- 📰 Blog articles (news updates, opinion pieces, how-to guides, listicles, post-editing)
- 🌐 Website content (homepage copy, about pages, product pages)
- And much more!
All that integrated seamlessly into our world-class task and project management workflow. ✨
And here’s the best part?
You can collaborate on translations with your team in real-time. All project members can use the /translate command and other AI tools and features simultaneously, without limitations.
Ready to break down language barriers and take your projects global?
🎯 Create a free Taskade account and or use one of our AI templates to get started.
🔗 Resources
- https://www.historyofinformation.com/detail.php?id=666
- https://mt-archive.net/70/T&T-1983-Pigott.pdf
- https://web.stanford.edu/class/archive/cs/cs224n/cs224n.1162/handouts/Collins_annotated.pdf
- https://ai.googleblog.com/2016/09/a-neural-network-for-machine.html
- https://blog.duolingo.com/how-duolingo-experts-work-with-ai/
- https://resources.unbabel.com/blog/new-report-global-trends-in-marketing-localization-for-2023
- https://csa-research.com/Blogs-Events/CSA-in-the-Media/Press-Releases/Consumers-Prefer-their-Own-Language
- https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11606-021-06666-z.pdf



 How AI Can Help You To Build A Second Brain: Revolutionizing Knowledge Management
How AI Can Help You To Build A Second Brain: Revolutionizing Knowledge Management  AI and Mind Mapping: Transforming Ideas Into Actionable Plans
AI and Mind Mapping: Transforming Ideas Into Actionable Plans  The 7 Best AI Image Generators of 2023: Unleashing the Power of AI
The 7 Best AI Image Generators of 2023: Unleashing the Power of AI  Unleashing the Future of AI in Programming: How Next-Gen AI Transforms Software Development
Unleashing the Future of AI in Programming: How Next-Gen AI Transforms Software Development  Rising Popularity of the 4-Day Workweek: Benefits, Implementation and Future
Rising Popularity of the 4-Day Workweek: Benefits, Implementation and Future  Get More Done with the PARA Method: A Productivity Framework for Organizing Your Life
Get More Done with the PARA Method: A Productivity Framework for Organizing Your Life